Is the Federal Funds Rate the Unsung Hero of the American Economy? The Federal Funds Rate, the overnight lending rate between banks, sits at the epicenter of U.S. monetary policy, subtly yet powerfully shaping the financial landscape.
The Federal Funds Rate, often referred to as the "fed funds rate," is the interest rate that banks charge each other for the overnight lending of reserve balances. These reserve balances are held by banks at the Federal Reserve. The Federal Reserve, the central bank of the United States, wields significant influence over this rate through its monetary policy decisions. The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), the monetary policymaking body of the Federal Reserve System, meets eight times a year to determine the target range for the federal funds rate. These meetings are crucial in setting the tone for the nation's financial health.
The mechanics of the Federal Funds Rate are relatively straightforward. When a bank needs to meet its reserve requirements, which are mandated by the Federal Reserve, it can borrow funds from another bank that has excess reserves. This borrowing occurs in the federal funds market, and the interest rate charged on these loans is the federal funds rate. The Federal Reserve doesnt directly set the federal funds rate; instead, it uses tools like open market operations to influence the supply of reserves in the banking system. By buying or selling government securities, the Fed can impact the availability of reserves and, consequently, the rate at which banks lend to each other.
- Nia Malika Hendersons Wife A Look Into The Life Of The Journalists Partner
- Understanding Mkvspoint Your Goto Resource For Movie Downloads
The interest rate on reserve balances (IORB rate) is another significant factor. This is the rate that the Federal Reserve pays banks on the balances they hold at the Fed. The IORB rate serves as a key tool in monetary policy, helping to establish a floor under the federal funds rate. By adjusting the IORB rate, the Federal Reserve can incentivize banks to maintain certain reserve levels, thereby influencing the overall cost of borrowing.
The Federal Reserve's decisions regarding the Federal Funds Rate have far-reaching effects. Changes in the rate influence other interest rates throughout the economy, including those for mortgages, car loans, and savings accounts. For instance, when the Federal Reserve raises the federal funds rate, it becomes more expensive for banks to borrow, which can lead to higher interest rates for consumers and businesses. Conversely, when the Fed lowers the rate, borrowing becomes cheaper, potentially stimulating economic activity. The Federal Reserve carefully assesses a variety of factors before making adjustments to the target range for the federal funds rate. These include incoming economic data, the evolving economic outlook, and the balance of risks to the economy. Data from sources like the Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis's FRED (Federal Reserve Economic Data) are vital, offering comprehensive economic indicators. FRED provides direct links to data releases and options to view charts, aiding in the analysis of trends and making informed decisions.
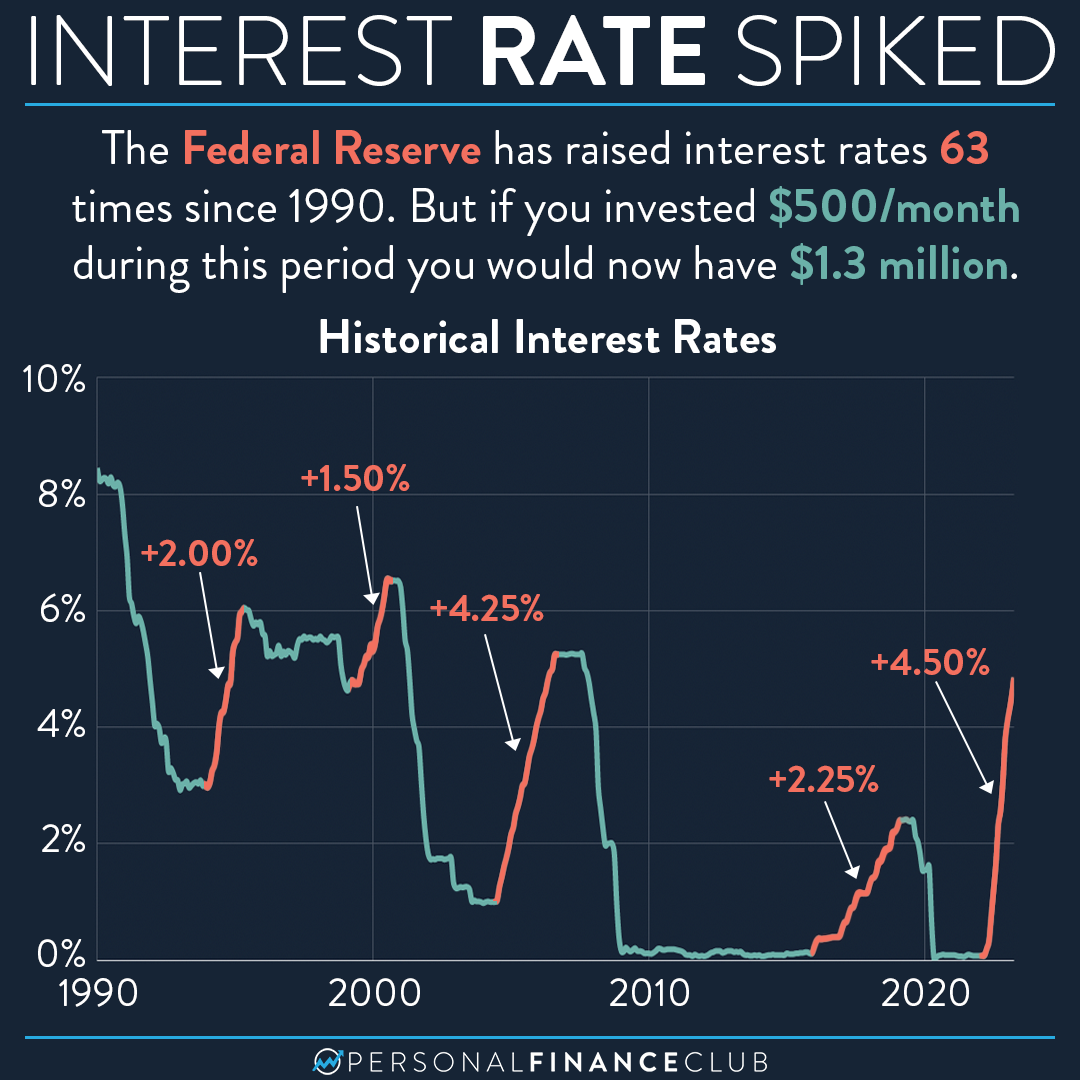
The Federal Reserve's commitment to stability is evident in its actions. The central bank aims to foster a safe, flexible, and stable monetary and financial system. In the face of economic fluctuations, the Federal Reserve often adjusts the Federal Funds Rate to guide the economy. For example, in 2022 and 2023, the Federal Reserve raised interest rates significantly to combat rising inflation. Subsequently, in late 2024, it eased rates, reflecting a shift in economic conditions. This demonstrates the dynamic nature of monetary policy and the Federal Reserve's willingness to respond to changing economic environments.
- Unveiling The Journey Of Sophie Rayin A Rising Star
- Nina Aouilk The Journey Of Her Parents And Their Impact On Her Life
The Federal Reserve Board of Governors in Washington, D.C., plays a central role in these processes. The board sets monetary policy, oversees the Federal Reserve Banks, and supervises the nation's banking system. The decisions made by the board, in conjunction with the FOMC, have broad implications for the U.S. economy. The Board and the Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis provide valuable resources for accessing and understanding economic data.
The Federal Reserve's H.15 release provides daily interest rates for various U.S. government and Federal Reserve series, offering crucial insights into market dynamics. This release is published every business day, except for holidays. The New York Fed also publishes the Effective Federal Funds Rate (EFFR) for the prior business day at approximately 9:00 a.m. on its website, offering a real-time view of the rate's daily movements. This continuous flow of information ensures that market participants and the public alike have access to up-to-date information about the Federal Funds Rate and its impact.
The Federal Funds Rate also interacts with the broader global financial system. With international trade and investment, decisions about the Federal Funds Rate can influence exchange rates and have repercussions for the global economy. For example, a rising Federal Funds Rate can make U.S. assets more attractive to foreign investors, potentially strengthening the dollar. However, this can also make U.S. exports more expensive, affecting trade balances.
The federal funds rate directly affects the borrowing costs for consumers and businesses, influencing economic growth, inflation, and employment. High federal funds rates can curb inflation by reducing spending and investment, while lower rates can spur economic activity by making borrowing cheaper. The Federal Reserve carefully weighs these competing goals when making its monetary policy decisions. The FOMCs projections for the federal funds rate, published in the Summary of Economic Projections, give markets and the public an indication of the committee's expectations and the potential future direction of monetary policy.
The Federal Funds Rate serves as a fundamental tool in the Federal Reserve's efforts to maintain price stability and promote maximum employment. These goals, mandated by Congress, shape the Feds approach to monetary policy. The ongoing monitoring of economic data, combined with a forward-looking approach, is crucial for the Federal Reserve in navigating the complex economic landscape. The Federal Reserve continues to refine its tools and strategies to achieve its monetary policy objectives and respond to the evolving needs of the U.S. economy.
The Federal Reserve's commitment to transparency helps ensure that market participants and the public are informed about its actions. The publication of meeting minutes, economic projections, and other communications provides a window into the decision-making processes. This helps to build trust and confidence in the central bank and its ability to manage the economy effectively.
The Federal Funds Rate is the interest rate at which depository institutions trade federal funds (balances held at federal reserve banks) with each other overnight. The Federal Reserve in a closely watched decision Wednesday held the line on benchmark interest rates though still indicated that reductions are likely later in the year. The current target range is 4.25% to 4.50%.
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | The interest rate at which depository institutions (mainly banks) lend reserve balances to other depository institutions overnight on an uncollateralized basis. |
| Influence | Influenced by the Federal Reserve through monetary policy decisions. |
| Target Range | Set by the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC). |
| Mechanism | Banks lend reserve balances to each other overnight in the federal funds market. |
| Tools of Influence | Open market operations (buying/selling government securities), interest rate on reserve balances (IORB). |
| Impact | Influences other interest rates, affects borrowing costs for consumers and businesses, influences economic growth, inflation, and employment. |
| FOMC Meetings | The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) meets eight times a year to determine the federal funds target rate. |
| Data Source | The Federal Reserve Board of Governors in Washington DC. Federal Reserve Economic Data (FRED). |
| Objective | To foster a safe, flexible, and stable monetary and financial system. Maintain price stability and promote maximum employment. |
| Publication | The New York Fed publishes the EFFR for the prior business day on the New York Feds website at approximately 9:00 a.m. The H.15 release contains daily interest rates for selected U.S. government and Federal Reserve series. |
| Related Terms | Interest rate on reserve balances (IORB rate). |
| Historical Data | Shows the daily level of the federal funds rate back to 1954. |
| Recent Developments | The federal reserve raised interest rates dramatically in 2022 and 2023, then eased them in late 2024. Washingtonthe federal reserve kept its key interest rate unchanged again wednesday and scaled back its forecast from three rate cuts to just one this year after an inflation pickup in early 2024. |
| Governing Body | The federal reserve board of governors in washington dc. |
For further details, you can refer to the official website of the Federal Reserve: Federal Reserve